This master qualifies for the profession of Industrial Engineer. Order CIN/311/2009*
*"Section 4.2.1 of the Annex declared null and void by Supreme Court Judgment (3rd Chamber, 4th Section) of October 30, 2012"
Responsible Center: Official Masters School Location: Mostoles Campus
Modality: Onsite Title code: 6258 Orientation: Approval
Number of ECTS Credits: 120 ECTS Duration of the Master: Two academic courses
Public prices: See table
Academic Calendar Schedule Examinations Teaching Guides Faculty
Director: Prof. Dr. D. Gabriel Morales Sánchez Co-director: Prof. Dr. Ms. Cristina Rodríguez Sánchez. Phone: 91 4888091
Master's website
E-mail:
University master's information: Phone: 91 665 5060 Inquiries Mailbox
Regulated profession for which it qualifies: Industrial Engineer (Order CIN/311/2009, of February 9)*
Student attention: Student Help Box Suggestions, complaints and congratulations mailbox
Basic Information
What knowledge will I acquire with this Master?
The proposed title of Master in Industrial Engineering incorporates in its curricular design all the professional attributions of the Industrial Engineer. Likewise, it pursues advanced training in the branches of engineering with a multidisciplinary nature. The Master's degree in Industrial Engineering that is proposed has been designed with the general objective of training Industrial Engineers prepared to enter the labor market with guarantees of employability and have the professional powers, regulated by law for the current Industrial Engineer. To this effect, the Master's degree proposed here strictly conforms to Ministerial Order CIN/311/2009, of February 9, 2009 (published in the BOE of February 18, 2009) which establishes the requirements for the verification of the official university degrees that qualify for the exercise of the profession of Industrial Engineer.
Is this degree official according to the regulations required by the European Higher Education Area?
Yes, (final verification report is attached) starting the first course in the academic year 2016-17.
Final verification report turned out FAVORABLE
Is it necessary to pass an access test?
No, although to access the master's degree, the requirements established by Ministerial Order CI/311/2009 and developed in the Study Plan verified by ANECA must be met.
What is the minimum number of credits for which I can enroll?
You can see it in the rules of permanence in this link
Recommended income profile
In accordance with Order CIN/311/2009, of February 9, which establishes the requirements for the verification of official university degrees that qualify for the exercise of the profession of Industrial Engineer*, and in addition to meeting the requirements established by article 16 of Royal Decree 1393/2007, the conditions of access to the Master are:
· It will be possible to access the Master's Degree when the degree certificate of the interested party certifies having completed the basic training module and the module common to the branch, even if not covering a complete block of the specific technology module, and if 48 credits of those offered in the set of the blocks of said module of a degree that qualifies for the exercise of Industrial Technical Engineer, in accordance with the aforementioned Ministerial Order.
· Likewise, those who have any other degree title may access this Master's degree, without prejudice to the establishment of any previous training complements deemed necessary in this case.
· The previous sections shall be understood, without prejudice to the provisions of article 17.2 and in the fourth additional provision of Royal Decree 1393/2007, of October 29, modified by Royal Decree 861/2010”.
*Article 4.2.1 of said Order is repealed according to Judgment TS (Room 3) of October 30, 2012.
Depending on the previous training accredited by the student, additional complements to the master's degree must be taken. These training complements will not be part of the master's degree. The body responsible for the master's degree will decide which additional training complements must be taken in each case.
Applications for access are assessed by the Master's Academic Committee (CAM). The Academic Committee takes into account the suitability of each applicant's access degree and their academic record to assign an access scale, for which it has among its components representatives of the areas involved in the teaching of the Master.
More specifically, it has been established that all the Bachelor's + Master's courses meet the following requirements:
· They must include at least 180 compulsory ECTS from the basic blocks common to the industrial branch and specific technology defined in ministerial order CIN/351/2009, covering at least 3 of the specific technology blocks.
· At least 24 ECTS, between bachelor's and master's degrees, must correspond to compulsory subjects that guarantee the specific competences of mathematics (including statistics), and at least 12 ECTS must correspond to compulsory subjects that guarantee the specific competences of physics. The aforementioned competencies refer to those included in the basic training module of CIN/351/2009.
· There must be at least 24 ECTS of intensification.
· They must contemplate a minimum of 24 ECTS, between the final degree project and the final master's degree.
In this way, only those candidates from Degrees other than Industrial Technology Engineering may be admitted, when they manage to meet the aforementioned requirements by enrolling in the Training Complements and Extension and Leveling subjects available and registered in the Verified Report. of the Master in Industrial Engineering (RUCT link).
Admission criteria:
Regarding admission, applications will be assessed by the Master's Academic Committee (CAM). According to the regulations of the Rey Juan Carlos University, the Academic Committee of the Master's Degree will be composed of at least the Director, two professors with permanent links to the URJC who teach the Master's Degree, a student enrolled in the Master's Degree, and a representative of the teaching staff. external or professionals participating in it. The Academic Commission will take into account the suitability of each applicant's access degree and their academic record to assign an access scale, for which it will include among its components representatives of the areas involved in the teaching of the Master.
Objectives
The general objective of the Master's Degree in Industrial Engineering is to train and specialize the student for the exercise of the regulated profession of Industrial Engineering. To this effect, the Master's degree proposed here strictly conforms to Ministerial Order CIN/311/2009, of February 9, 2009 (published in the BOE of February 18, 2009) which establishes the requirements for the verification of the official university degrees that qualify for the exercise of the profession of Industrial Engineer.
Competences
BASIC SKILLS
- CB6 - Possess and understand knowledge that provides a basis or opportunity to be original in the development and/or application of ideas, often in a research context
- CB7 - That students know how to apply the knowledge acquired and their ability to solve problems in new or little-known environments within broader (or multidisciplinary) contexts related to their area of study
- CB8 - That students are able to integrate knowledge and face the complexity of formulating judgments based on information that, being incomplete or limited, includes reflections on the social and ethical responsibilities linked to the application of their knowledge and judgments
- CB9 - That students know how to communicate their conclusions and the knowledge and ultimate reasons that support them to specialized and non-specialized audiences in a clear and unambiguous way
- CB10 - That students have the learning skills that allow them to continue studying in a way that will be largely self-directed or autonomous
GENERAL COMPETENCIES
|
Custom code |
Description |
|
CG1 |
Have adequate knowledge of the scientific and technological aspects of: mathematical, analytical and numerical methods in engineering, electrical engineering, energy engineering, chemical engineering, mechanical engineering, continuum mechanics, industrial electronics, automation, manufacturing, materials, quantitative methods of management, industrial computing, urban planning, infrastructure, etc. |
|
CG2 |
Project, calculate and design products, processes, installations and plants. |
|
CG3 |
Lead, plan and supervise multidisciplinary teams. |
|
CG4 |
Carry out research, development and innovation in products, processes and methods |
|
CG5 |
Carry out strategic planning and apply it to both construction and production, quality and environmental management systems. |
|
CG6 |
Technically and economically manage projects, facilities, plants, companies and technology centers. |
|
CG7 |
Being able to perform functions of general management, technical management and management of R&D&i projects in plants, companies and technology centres. |
|
CG8 |
Apply the knowledge acquired and solve problems in new or little-known environments within broader and multidisciplinary contexts. |
|
CG9 |
Being able to integrate knowledge and face the complexity of formulating judgments based on information that, being incomplete or limited, includes reflections on the social and ethical responsibilities linked to the application of their knowledge and judgments. |
|
CG10 |
Knowing how to communicate the conclusions –and the knowledge and ultimate reasons that support them– to specialized and non-specialized audiences in a clear and unambiguous way. |
|
CG11 |
Possess the learning skills that allow them to continue studying in a self-directed or autonomous way. |
|
CG12 |
Knowledge, understanding and ability to apply the necessary legislation in the exercise of the profession of Industrial Engineer. |
TRANSVERSAL COMPETENCES
|
Custom code |
Description |
|
CT1 |
Apply scientific, mathematical and technological knowledge in systems related to the practice of engineering. |
|
CT2 |
Design and conduct experiments, and analyze and interpret data |
|
CT3 |
Design a system, component or process that meets the desired requirements taking into account realistic economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturing and sustainability constraints. |
|
CT4 |
Work in multidisciplinary teams. |
|
CT5 |
Ability to identify, formulate and solve engineering problems. |
|
CT6 |
Understand ethics and professional responsibility. |
|
CT7 |
Know how to communicate effectively. |
|
CT8 |
Being able to integrate knowledge to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global social context. |
|
CT9 |
Develop continuous learning skills. |
|
CT10 |
Possess knowledge of contemporary issues. |
|
CT11 |
Use the techniques, skills and modern tools necessary for the practice of engineering. |
|
CT12 |
Direct, organize and plan projects and human teams in the field of the company, and other institutions and organizations. |
|
CT13 |
Apply the knowledge acquired to develop creative engineering solutions. |
SPECIFIC COMPETENCES
|
Custom code |
Description |
|
CE1 |
Knowledge and ability to analyze and design electrical generation, transport and distribution systems. |
|
CE2 |
Knowledge and ability to project, calculate and design integrated manufacturing systems. |
|
CE3 |
Ability to design and test machines. |
|
CE4 |
Ability to analyze and design chemical processes. |
|
CE5 |
Knowledge and skills for the design and analysis of thermal machines and engines, hydraulic machines and industrial heating and cooling installations. |
|
CE6 |
Knowledge and skills that allow understanding, analysing, exploiting and managing the different energy sources. |
|
CE7 |
Ability to design electronic systems and industrial instrumentation. |
|
CE8 |
Ability to design and project automated production systems and advanced process control. |
|
CE9 |
Knowledge and skills to organize and direct companies. |
|
CE10 |
Knowledge and skills of strategy and planning applied to different organizational structures. |
|
CE11 |
Knowledge of commercial and labor law. |
|
CE12 |
Knowledge of financial and cost accounting. |
|
CE13 |
Knowledge of management information systems, industrial organization, production and logistics systems, and quality management systems. |
|
CE14 |
Capacities for work organization and human resource management. Knowledge of occupational risk prevention. |
|
CE15 |
Knowledge and skills for integrated project management. |
|
CE16 |
Ability to manage research, development and technological innovation. |
|
CE17 |
Ability to design, build and operate industrial plants. |
|
CE18 |
Knowledge of construction, building, facilities, infrastructure and urban planning in the field of industrial engineering. |
|
CE19 |
Knowledge and skills for the calculation and design of structures. |
|
CE20 |
Knowledge and skills to project and design electrical and fluid installations, lighting, air conditioning and ventilation, energy saving and efficiency, acoustics, communications, home automation and intelligent buildings and security installations. |
|
CE21 |
Knowledge of industrial transport and maintenance methods and techniques. |
|
CE22 |
Knowledge and skills to perform verification and control of facilities, processes and products. |
|
CE23 |
Knowledge and skills to carry out certifications, audits, verifications, tests and reports. |
|
CE24 |
Completion, presentation and public defense, once all the credits of the study plan have been obtained, of an original exercise carried out individually before a university tribunal, consisting of a comprehensive Industrial Engineering project of a professional nature in which the skills acquired in the teachings. |
Admission and enrollment
Admission:
The requirements for access to the proposed title are according to article 18, of Royal Decree 822/2021, of September 28:
- Possession of an official Spanish Graduate or Graduate university degree or equivalent is a condition for accessing a Master's Degree, or, where appropriate, having another University Master's degree, or titles of the same level as the Spanish Bachelor's or Master's degree issued by universities and higher education institutions in an EHEA country that in that country allow access to Master's degrees.
- In the same way, people in possession of titles from educational systems that are not part of the EHEA, which are equivalent to a Bachelor's degree, will be able to access a Master's Degree in the Spanish university system, without the need for homologation of the title, but verification by of the university of the level of training that they imply, as long as in the country where said title was issued it allows access to university postgraduate level studies. In no case will access through this route imply the homologation of the previous degree held by the person concerned or its recognition for other purposes than that of carrying out the Master's degree.
Candidate selection:
Applications will be assessed by the Master's Academic Committee (CAM), which will take into account the suitability of each applicant's access degree (50%) and their academic record (50%) to assign an access scale.
Offer of places: 60 seats. If the minimum number of students envisaged is not reached in a course, the University may choose not to open the teaching group.
Training itinerary
Master's Teaching Guides
ACCESS THE COURSE GUIDES OF THE DEGREE
Training Itinerary
Itinerary 1: Degree in Industrial Technology Engineering (GITI)
|
Custom code |
Name of the module or matter |
ECTS credits |
semester |
Character |
|
MODULE I: Industrial Technologies |
36 |
required |
||
|
625801 |
Applied Electrical Engineering |
4,5 |
1° |
required |
|
625802 |
Integrated Manufacturing Processes |
4,5 |
1° |
required |
|
625803 |
Machine Technology |
4,5 |
1° |
required |
|
625804 |
Analysis and Design of Chemical Processes |
4,5 |
1° |
required |
|
625805 |
Thermal Engineering |
4,5 |
2° |
required |
|
625806 |
Energy Systems |
4,5 |
2° |
required |
|
625807 |
Applied Electronics |
4,5 |
2° |
required |
|
625808 |
Discreet control |
4,5 |
2° |
required |
|
MODULE II: Management |
15 |
required |
||
|
625809 |
Business Management |
6 |
1° |
required |
|
625810 |
Production and Logistics Systems |
3 |
3° |
required |
|
625811 |
Project Management and R&D Management |
6 |
2° |
required |
|
MODULE III: Installations, plants and complementary constructions |
15 |
required |
||
|
625812 |
Design of Structures and Industrial Constructions |
6 |
1° |
required |
|
625813 |
Industrial facilities |
6 |
2° |
required |
|
625814 |
Industrial maintenance |
3 |
3° |
required |
|
MODULE V: Specialty3 |
30 (max) |
(Choose 5 subjects) |
Optional |
|
|
625815 * |
Transportation Technologies (A-Specialization in Mechanical Engineering/G-Specialization in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625816 * |
Structural Integrity (A-Mechanical Engineering Specialty) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625817 * |
Design and Analysis of Mechanical Systems (A-Specialty in Mechanical Engineering/I-Specialty in Electromechanical Systems) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625818 * |
Artificial Vision (B-Specialty in Electronic Engineering) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625819 * |
Monitoring and Control Systems (B-Specialty in Electronic Engineering / I-Specialty in Electromechanical Systems) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625820 * |
Digital devices and microelectronics (B-Specialization in Electronic Engineering) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625821 |
Strategy in Process Engineering (C-Specialization in Chemical Engineering/H-Specialization in Advanced Production) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625822 |
Simulation and Optimization of Processes (C-Specialty in Chemical Engineering) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625823 * |
Clean Fuels for Sustainable Transportation (C-Specialization in Chemical Engineering/G-Specialization in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625824 * |
Energy Efficiency (D-Specialization in Energy Sustainability) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625825 * |
Efficient Energy Storage Systems (D-Specialization in Energy Sustainability / G-Specialization in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625826 * |
Cogeneration, Combined Cycles and Industrial Energy Optimization (D-Specialization in Energy Sustainability) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625827 |
Ecodesign and Life Cycle Analysis (E-Specialty in Environmental Management in Industry/H-Specialty in Advanced Production) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625828 |
Environmental Impact Assessment (E-Specialty in Environmental Management in Industry) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625829 |
Management and Treatment of Waste and Industrial Effluents (E-Specialty in Environmental Management in Industry) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625830 |
Composite Materials (F-Major in Materials and Manufacturing) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625831 |
Light Alloys (F-Specialty in Materials and Manufacturing) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625832 * |
Materials for Air and Surface Transportation Systems (F-Specialty in Materials and Manufacturing G-Specialty in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
625833 |
Advanced Manufacturing Processes (H-Specialty in Advanced Production/I-Specialty in Electromechanical Systems) |
6 |
3rd and 4th |
Optional |
|
MODULE VI: External Practices |
12 |
External Internships |
||
|
625834 * |
External Internships |
12 |
3° |
External Internships |
|
MODULE VII: Master's thesis |
12 |
required |
||
|
- |
Master's thesis |
12 |
4° |
required |
|
1: Semester in which it is studied, according to the itinerary: Itinerary 1 / Itinerary 2a / Itinerary 2b. 2: Subjects to study for students of Itinerary 2 (a and b). The number of credits and subjects to be taken is determined by the Master's Academic Committee according to the graduate's previous training and the access route to the Master's Degree. 3: Specialty subjects to be taken by students on Itinerary 1 and 2a and 2b. The number of credits and subjects to be taken is determined by the Master's Academic Committee according to the graduate's previous training and the access route to the Master's Degree. |
||||
Itinerary 2:
Itinerary 2a:
- Degree in Chemical Engineering (GIQ)
- Degree in Materials Engineering (GIMat)
- Degree in Energy Engineering (GIEnE)
- Degree in Mechanical Engineering
- Degree in Electronic and Automatic Engineering
+ TRAINING COMPLEMENTS
|
Custom code |
Name of the module or matter |
ECTS credits |
semester |
Character |
|
MODULE I: Industrial Technologies |
36 |
required |
||
|
625801 |
Applied Electrical Engineering |
4,5 |
3° |
required |
|
625802 |
Integrated Manufacturing Processes |
4,5 |
3° |
required |
|
625803 |
Machine Technology |
4,5 |
3° |
required |
|
625804 |
Analysis and Design of Chemical Processes |
4,5 |
3° |
required |
|
625805 |
Thermal Engineering |
4,5 |
4° |
required |
|
625806 |
Energy Systems |
4,5 |
4° |
required |
|
625807 |
Applied Electronics |
4,5 |
4° |
required |
|
625808 |
Discreet control |
4,5 |
4° |
required |
|
MODULE II: Management |
15 |
required |
||
|
625809 |
Business Management |
6 |
3° |
required |
|
625810 |
Production and Logistics Systems |
3 |
5° |
required |
|
625811 |
Project Management and R&D Management |
6 |
2° |
required |
|
MODULE III: Installations, plants and complementary constructions |
15 |
required |
||
|
625812 |
Design of Structures and Industrial Constructions |
6 |
3° |
required |
|
625813 |
Industrial facilities |
6 |
2° |
required |
|
625814 |
Industrial maintenance |
3 |
5° |
required |
|
MODULE IV: Expansion and Leveling2 |
24 (max) |
Optional |
||
|
625860* |
Structures and Manufacturing |
6 |
2° |
Optional |
|
625842 * |
Chemical Processes and Products |
6 |
2° |
Optional |
|
625861* |
Electric Machines |
6 |
2° |
Optional |
|
625844 * |
Electronic systems |
6 |
2° |
Optional |
|
MODULE V: Specialty3 |
30 (max) |
Optional |
||
|
625815 * |
Transportation Technologies (A-Specialization in Mechanical Engineering/G-Specialization in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625816 * |
Structural Integrity (A-Mechanical Engineering Specialty) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625817 * |
Design and Analysis of Mechanical Systems (A-Specialty in Mechanical Engineering/I-Specialty in Electromechanical Systems) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625818 * |
Artificial Vision (B-Specialty in Electronic Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625819 * |
Monitoring and Control Systems (B-Specialty in Electronic Engineering / I-Specialty in Electromechanical Systems) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625820 * |
Digital devices and microelectronics (B-Specialization in Electronic Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625821 |
Strategy in Process Engineering (C-Specialization in Chemical Engineering/H-Specialization in Advanced Production) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625822 |
Simulation and Optimization of Processes (C-Specialty in Chemical Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625823 * |
Clean Fuels for Sustainable Transportation (C-Specialization in Chemical Engineering/G-Specialization in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625824 * |
Energy Efficiency (D-Specialization in Energy Sustainability) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625825 * |
Efficient Energy Storage Systems (D-Specialization in Energy Sustainability / G-Specialization in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625826 * |
Cogeneration, Combined Cycles and Industrial Energy Optimization (D-Specialization in Energy Sustainability) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625827 |
Ecodesign and Life Cycle Analysis (E-Specialty in Environmental Management in Industry/H-Specialty in Advanced Production) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625828 |
Environmental Impact Assessment (E-Specialty in Environmental Management in Industry) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625829 |
Management and Treatment of Waste and Industrial Effluents (E-Specialty in Environmental Management in Industry) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625830 |
Composite Materials (F-Major in Materials and Manufacturing) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625831 |
Light Alloys (F-Specialty in Materials and Manufacturing) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625832 * |
Materials for Air and Surface Transportation Systems (F-Specialty in Materials and Manufacturing G-Specialty in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625833 |
Advanced Manufacturing Processes (H-Specialty in Advanced Production/I-Specialty in Electromechanical Systems) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
MODULE VI: External Practices |
12 |
External Internships |
||
|
625834 * |
External Internships |
12 |
5° |
External Internships |
|
MODULE VII: Master's thesis |
12 |
required |
||
|
- |
Master's thesis |
12 |
5° |
required |
|
||||
Itinerary 2:
Route 2b:
- Degree in Industrial Organization (GIOI)
- Degree in Environmental Engineering (GIA)
+ TRAINING COMPLEMENTS
|
Custom code |
Name of the module or matter |
ECTS credits |
semester |
Character |
|
MODULE I: Industrial Technologies |
36 |
required |
||
|
625801 |
Applied Electrical Engineering |
4,5 |
3° |
required |
|
625802 |
Integrated Manufacturing Processes |
4,5 |
3° |
required |
|
625803 |
Machine Technology |
4,5 |
3° |
required |
|
625804 |
Analysis and Design of Chemical Processes |
4,5 |
3° |
required |
|
625805 |
Thermal Engineering |
4,5 |
4° |
required |
|
625806 |
Energy Systems |
4,5 |
4° |
required |
|
625807 |
Applied Electronics |
4,5 |
4° |
required |
|
625808 |
Discreet control |
4,5 |
4° |
required |
|
MODULE II: Management |
15 |
required |
||
|
625809 |
Business Management |
6 |
3° |
required |
|
625810 |
Production and Logistics Systems |
3 |
5° |
required |
|
625811 |
Project Management and R&D Management |
6 |
2° |
required |
|
MODULE III: Installations, plants and complementary constructions |
15 |
required |
||
|
625812 |
Design of Structures and Industrial Constructions |
6 |
3° |
required |
|
625813 |
Industrial facilities |
6 |
4° |
required |
|
625814 |
Industrial maintenance |
3 |
5° |
required |
|
MODULE IV: Expansion and Leveling2 |
24 (max) |
Optional |
||
|
625860* |
Machines, Structures and Manufacturing |
6 |
2° |
Optional |
|
625842 * |
Chemical Processes and Products |
6 |
2° |
Optional |
|
625843 |
Electric engineering |
6 |
2° |
Optional |
|
625844 * |
Electronic systems |
6 |
2° |
Optional |
|
MODULE V: Specialty3 |
30 (max) |
Optional |
||
|
625815 * |
Transportation Technologies (A-Specialization in Mechanical Engineering/G-Specialization in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625816 * |
Structural Integrity (A-Mechanical Engineering Specialty) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625817 * |
Design and Analysis of Mechanical Systems (A-Specialty in Mechanical Engineering/I-Specialty in Electromechanical Systems) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625818 * |
Artificial Vision (B-Specialty in Electronic Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625819 * |
Monitoring and Control Systems (B-Specialty in Electronic Engineering / I-Specialty in Electromechanical Systems) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625820 * |
Digital devices and microelectronics (B-Specialization in Electronic Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625821 |
Strategy in Process Engineering (C-Specialization in Chemical Engineering/H-Specialization in Advanced Production) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625822 |
Simulation and Optimization of Processes (C-Specialty in Chemical Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625823 * |
Clean Fuels for Sustainable Transportation (C-Specialization in Chemical Engineering/G-Specialization in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625824 * |
Energy Efficiency (D-Specialization in Energy Sustainability) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625825 * |
Efficient Energy Storage Systems (D-Specialization in Energy Sustainability / G-Specialization in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625826 * |
Cogeneration, Combined Cycles and Industrial Energy Optimization (D-Specialization in Energy Sustainability) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625827 |
Ecodesign and Life Cycle Analysis (E-Specialty in Environmental Management in Industry/H-Specialty in Advanced Production) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625828 |
Environmental Impact Assessment (E-Specialty in Environmental Management in Industry) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625829 |
Management and Treatment of Waste and Industrial Effluents (E-Specialty in Environmental Management in Industry) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625830 |
Composite Materials (F-Major in Materials and Manufacturing) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625831 |
Light Alloys (F-Specialty in Materials and Manufacturing) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
625832 * |
Materials for Air and Surface Transportation Systems (F-Specialty in Materials and Manufacturing G-Specialty in Transportation Engineering) |
6 |
4 º |
Optional |
|
625833 |
Advanced Manufacturing Processes (H-Specialty in Advanced Production/I-Specialty in Electromechanical Systems) |
6 |
4° |
Optional |
|
MODULE VI: External Practices |
12 |
External Internships |
||
|
625834 * |
External Internships |
12 |
5 º |
External Internships |
|
MODULE VII: Master's thesis |
12 |
required |
||
|
- |
Master's thesis |
12 |
5° |
required |
|
1: Semester in which it is studied, according to the itinerary: Itinerary 1 / Itinerary 2a / Itinerary 2b. 2: Subjects to study for students of Itinerary 2 (a and b). The number of credits and subjects to be taken is determined by the Master's Academic Committee according to the graduate's previous training and the access route to the Master's Degree. 3: Specialty subjects to be taken by students on Itinerary 1 and 2a and 2b. The number of credits and subjects to be taken is determined by the Master's Academic Committee according to the graduate's previous training and the access route to the Master's Degree. |
||||
* Offered in the 2021-22 academic year
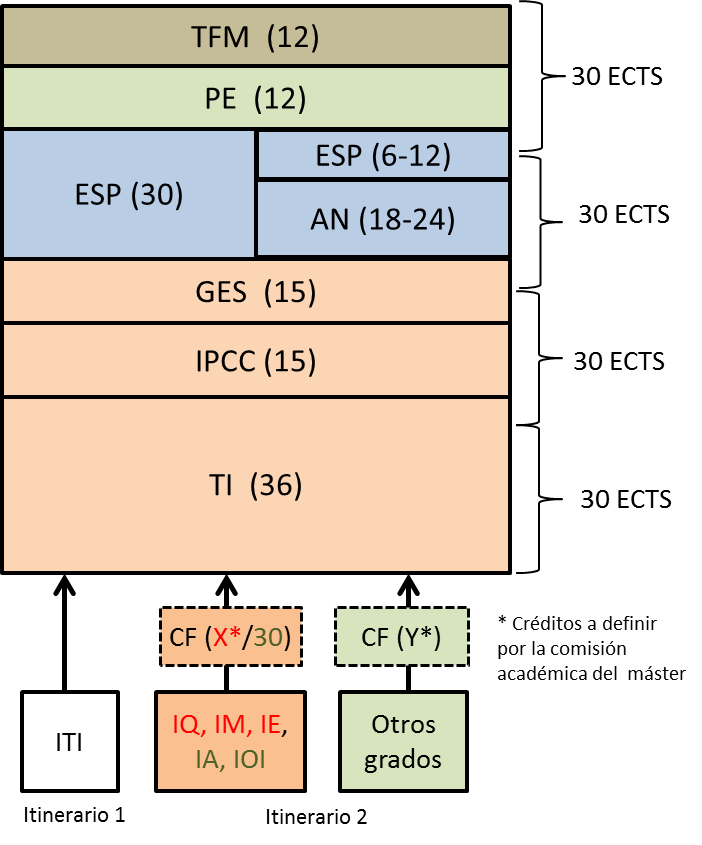
Figure 5.1 schematically represents the distribution of modules, itineraries and access routes.
|
|
Figure 5.1. Scheme of access routes and itineraries of the master's degree.
The specific contents of the modules are detailed below.
Module I: Industrial Technologies, IT (36 ECTS)
It is made up of 8 subjects that cover the 8 specific skills described in order CIN/311/2009:
Applied Electrical Engineering. 4,5 ECTS. Competencies: Knowledge and ability to analyze and design electrical generation, transport and distribution systems.
Integrated Manufacturing Processes. 4,5 ECTS. Competencies: Knowledge and ability to project, calculate and design integrated manufacturing systems.
Machine Technology. 4,5 ECTS. Competencies: Ability to design and test machines.
Analysis and Design of Chemical Processes. 4,5 ECTS. Competencies: Ability to analyze and design chemical processes.
Thermal Engineering. 4,5 ECTS. Competencies: Knowledge and skills for the design and analysis of thermal machines and engines, hydraulic machines and industrial heating and cooling installations.
Energy Systems. 4,5 ECTS. Competencies: Knowledge and skills that allow understanding, analysing, exploiting and managing the different energy sources.
Applied Electronics. 4,5 ECTS. Competencies: Ability to design electronic systems and industrial instrumentation.
Discreet control. 4,5 ECTS. Competencies: Ability to design and project automated production systems and advanced process control.
Module II: Management, GES (15 ECTS)
It is made up of 3 subjects that cover the 8 skills described in order CIN/311/2009:
Business Management. 6 ECTS. Competencies: Knowledge and skills to organize and direct companies. Knowledge of commercial and labor law. Knowledge of financial and cost accounting. Capacities for human resources management.
Production and Logistics Systems. 3 ECTS. Competencies: Knowledge of management information systems, industrial organization, production and logistics systems, and quality management systems. Capacities for work organization. Knowledge of occupational risk prevention.
Project Management and R&D Management. 6 ECTS. Competencies: Knowledge and skills of strategy and planning applied to different organizational structures. Knowledge and skills for integrated project management. Ability to manage research, development and technological innovation.
Module III: Installations, Plants and Complementary Constructions, IPCC (15 ECTS)
It is made up of 3 subjects that cover the 7 skills described in order CIN/311/2009:
Design of Structures and Industrial Constructions. 6 ECTS. Competencies: Ability to design and build industrial plants. Knowledge of construction, building, in the field of industrial engineering. Knowledge and skills for the calculation and design of structures. Knowledge of industrial transport and maintenance methods and techniques.
Industrial facilities. 6 ECTS. Competencies: Ability to operate industrial plants. Knowledge of facilities, infrastructure and urban planning in the field of industrial engineering. Knowledge and skills to project and design electrical and fluid installations, lighting, air conditioning and ventilation, energy saving and efficiency, acoustics, communications, home automation and intelligent buildings and security installations. Knowledge and skills to control facilities, processes and products.
Industrial maintenance. 3 ECTS. Competencies: Knowledge and skills to verify facilities, processes and products. Knowledge and skills to carry out certifications, audits, verifications, tests and reports.
Module IV: Extension and Levelling, AN (maximum of 30 ECTS)
This block must be compulsorily completed by the students of itinerary 2. It is designed to cover the training deficiencies that the student has corresponding to common subjects of the industrial branch previously studied in the Degree or in the previous training complements, taking the degree as a reference. GITI of the URJC, and in no case will it exceed 30 ECTS. It will be defined by the Master's Academic Committee based on the training for access to the master's degree. However, for the ESCET degrees, 9 subjects have been defined with which both the previous training supplements and the subjects of expansion and leveling of the specific itinerary for each degree of the School can be configured (GIOI, Engineering in Industrial Organization ; GIA, Environmental Engineering; GIEne, Energy Engineering; GIMat, Materials Engineering; GIQ, Chemical Engineering):
|
ENLARGEMENT AND LEVELING MODULE |
||||||
|
Subject |
ECTS |
GIO* |
GIA* |
GIene |
GImat |
GIQ |
|
Machines, Structures and Manufacturing |
6 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
Chemical Processes and Products |
6 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
Electric engineering |
6 |
X |
X |
X |
||
|
Electronic systems |
6 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
Total credits |
24 (54) |
24 (48) |
42 |
42 |
42 |
|
For access from other degrees in the field of engineering, the Master's Academic Committee will be in charge of preparing the appropriate itinerary (considering the appropriate Training Complements) based on the student's previous training.
Module V: Specialty (maximum of 30 ECTS)
In the specialty module, a set of subjects are offered among which the student must take a maximum of 30 ECTS, and which will reinforce the acquisition of the skills worked on in the compulsory modules. The offer will be grouped into nine Industrial Engineering specialty blocks: Mechanical Engineering, Electronic Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Energy Sustainability, Environmental Management in Industry, Materials and Manufacturing, Transport Engineering, Advanced Production and Electromechanical Systems.
This module will be taken by students but to a different extent. Itinerary 1 students will take the maximum (30 ECTS), and for Itinerary 2 the number of credits will be equal to the difference between 30 and the number of credits of the Expansion Module that they have to take.
In the event that the student takes 18 ECTS within one of the specialty blocks and develops his Master's Thesis of 12 ECTS in a subject from that same block, said specialty will be reflected in his university degree. If a student takes the necessary credits to cover more than one specialty, she can only have the mention of one of them in her title, as defined by the theme of the Master's Thesis that she carries out.
Table 5.2 shows the specialty subjects offered, grouped into the corresponding nine Specialty Blocks considered. 6 pure Specialties are considered, which offer 3 subjects of 6 ECTS each. They are the following:
- Specialty A: Mechanical Engineering
- Specialty B: Electronic Engineering
- Specialty C: Chemical Engineering
- Specialty D: Energy Sustainability
- Specialty E: Environmental Management in Industry
- Specialty F: Materials and Manufacturing
In addition, 3 Specialties are offered consisting of a combination of subjects from the above:
- Specialty G: Transportation Engineering
- Specialty H: Advanced Production
- Specialty I: Electromechanical Systems
Finally, it is necessary to take into account the close collaboration established between the Rey Juan Carlos University and the University of Alcalá with the “Intelligent Energy” Campus of International Excellence. Among the objectives of this collaboration is to integrate the capacities of both university communities in a training, scientific and professional development offer around Clean Energies and "Smart Cities", which opens a framework for academic collaboration that allows expanding the offer for students of both universities.
In this context, in addition to the specialties offered at the ESCET of the Rey Juan Carlos University, the students of the Master in Industrial Engineering of the URJC will be able to access the optional subjects that the University of Alcalá offers to the students of its Master in Industrial Engineering . These subjects are grouped into two specialties:
- Robotics and perception
- Smart power generation and distribution
In the same way, the students of the Master in Industrial Engineering of the University of Alcalá will be able to access the optional subjects of the Master in Industrial Engineering of the Rey Juan Carlos University.
To facilitate the teaching of these elective subjects, and that students from both Universities can attend without traveling, you can make use of the twin tele-teaching classrooms existing in both Universities and that have been installed with the help of infrastructures from the Campus of International Excellence "Energy Intelligent". Both classrooms have compatible technologies equipped with "streaming" systems to be able to record and retransmit classes in real time. The adaptation and recognition of the credits taken by the students between the two universities will be carried out in accordance with the agreements and regulations in force at both universities.
External Internships
The External Practices subject is a curricular subject whose main objective is to promote a comprehensive training of the student through the practical application of the knowledge acquired during the master's degree, which facilitates direct contact with the professional activity and the opportunity to join the professional world with a minimum of experience. All practices are designed so that the students who participate in them acquire professional experience in real situations and conditions, applying the knowledge, skills and attitudes that are acquired in the training processes throughout the degree. The internships represent a decisive opportunity for the personal development and professional future of the students.
Internships are activities carried out by the student in companies, institutions and organizations; that is, in centers outside the university premises, which aim to enrich and complement your university education, while providing you with a deeper knowledge about the skills you will need once you have graduated.
The External Practices subject will consist of two phases:
- Completion of the internship period that offers professional experience related to any of the graduate profiles that are expressed in the Verification Report of the degree.
- Elaboration of the memory
Documentation:
Degree Training Project
For more information: External Internship Unit
Social Security contributions for interns starting January 1, 2024
Mobility programs
University Master's degrees, due to their duration and characteristics, in general do not specifically contemplate the mobility of their students. However, the Rey Juan Carlos University has different mobility programs for both students and University workers (PDI and PAS) and has procedures for collecting and analyzing information on these mobility programs.
Regulation
- Academic Calendar
- Regulations for enrollment and permanence in university master's degrees at the URJC
- academic waiver
- Public prices for university master's degrees
- Exemption from the prices of official master's and doctoral studies for the sons and daughters under 25 years of age of victims of gender violence
- External Internships
- University Master's Thesis
- Review and Complaint of the Continuous Evaluation in the studies of university master's degrees of the URJC
- Acknowledgments / Adaptations of university master's degrees
- Simultaneity of URJC university master's degree studies
- Regulations of the School of Official Masters
- Addendum to the protocol for adapting teaching at the School of Official Master's Degrees
- Royal Decree 1125/2003, of September 5, which establishes the European credit system and the qualification system in official university degrees valid throughout the national territory
STUDENTS
COEXISTENCE REGIME
SCHOOL INSURANCE
ASSOCIATIONS
Quality guarantee
Results report
Once the monitoring of the Master's Degree has been carried out, the most relevant quantitative information on the results obtained in the monitoring of said Degree is displayed, differentiated by academic year.
Reports by course:
General information collection plan
Within the quality assurance system of the Rey Juan Carlos University, the following surveys are planned:
- Student profile
- Teacher evaluation
- Degree of satisfaction:
- Of the students
- of the graduates
- From the Faculty
- Administration and Services Staff
- Labor insertion
- External internships:
- Satisfaction of interns
- External tutor satisfaction
- Employer satisfaction
Survey results:
Improvement actions
The Quality Assurance System of the Rey Juan Carlos University establishes that the degree's Quality Assurance Commission will annually analyze the information derived from the degree's indicators and prepare a report that will include improvement plans if the results so indicate.
Renewal of accreditation
The renewal of the accreditation represents the culmination of the implementation process of the official Bachelor's and Master's degrees registered in the Register of Universities, Centers and Degrees (RUCT). The renewal of the accreditation of official bachelor's and master's degrees is organized in three phases: self-assessment report, external visit and final assessment.
In the first phase, the university describes and assesses the status of the degree with respect to the established criteria and guidelines. The result is the Self-Assessment Report (IA) that is presented. The second and third phases are carried out by a group of evaluators external to the evaluated title.”