Branch of knowledge: Engineering and architecture
Responsible Center: Higher Technical School of Computer Engineering
Teaching modality and Campus: Face-to-face Móstoles
Double degree with: Informatics Engineering, Video Game Design and Development
Credits: 240. Credits year: 60. Duration: 4 years. Implantation: progressive, first year 2009-2010
Academic Calendar Schedule Exams Teaching Guides Validation table Faculty
Coordinator: Prof. Dr. D. Carlos Garre del Olmo
| International seal of quality EURO-INF |
 |
Student attention: 91 488 93 93. Student Help Box Suggestions, complaints and congratulations mailbox
Basic Information
What knowledge will I acquire with this Degree?
The Computer Engineer will have as main missions the design, configuration, sizing, maintenance, operation and updating of data processing equipment, as well as the development of new applications, systems and products based on the efficient use of computers or digital processors. Regarding the type of systems, they will be the competence of Computer Engineers from small embedded systems of low cost and consumption, to complex networks of high-performance equipment.
Where will I be able to work when I graduate?
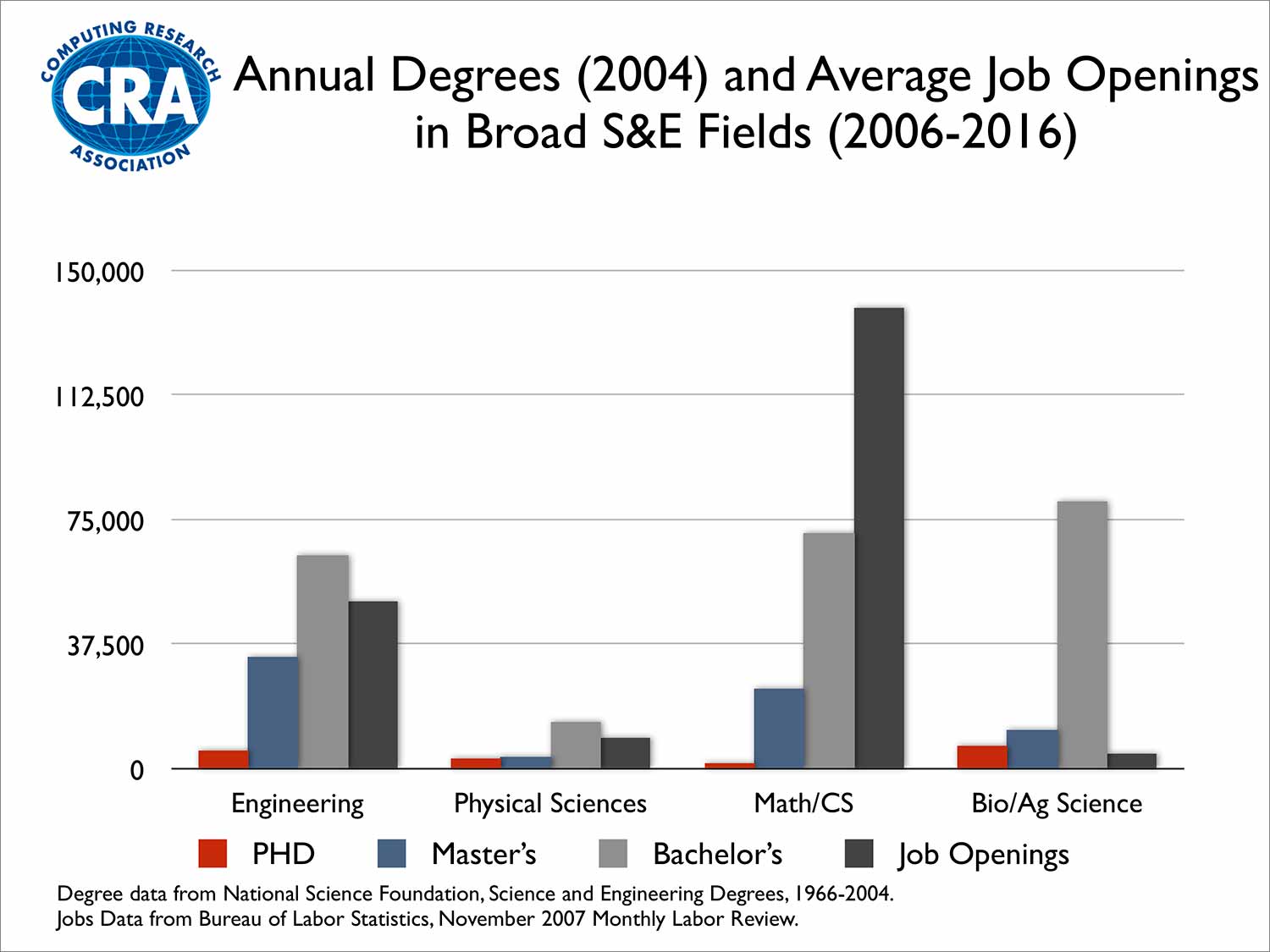
The professional opportunities that the market has historically offered to computer science graduates, including those who have worked as Computer Engineers (Computer Engineers specialized in systems, communications, high-performance architectures and embedded systems, but also physicists and other engineers related to specialties of Electricity, Automation or Telecommunications), are extremely positive. Both nationally and internationally, the demand for Computer Engineers has not stopped increasing in recent years, currently standing at the top of the labor market. The already mentioned presence of computer systems in practically all areas (financial, industrial, health, etc.) means that this demand continues to increase, causing a deficit of Computer Engineers. In the European Union, data provided by the ITC Consortium (IBM, Nokia, Philips, Thomson, Siemens, Microsoft Europe, British Telecom) estimated the shortage of professionals in 2003 at 2.362.000. By country, the deficit in Spain would be 83.538 professionals. If the situation in the United States is analyzed, the results are similar. Below is a graphical presentation of the relationship between graduate students and job demand for different profiles (according to the "National Science Foundation" and "Bureau of Labor Statistics"), including Engineering in general and more specifically Computer Sciences ”). As can be seen in the case of Computer Science, the labor demand (in dark grey) is enormously higher than the number of graduates (in light grey). If compared with the rest of the profiles present in the graph, the need to continue training specialists in Computer Science in general, including the area covered by graduates in Computer Engineering, is clear.
 |
Is this Degree official according to the regulations required by the European Higher Education Area?
Yes (final verification report is attached), the implementation of the degree will be done progressively, starting the first year in the academic year 2009-10.
The final verification report turned out FAVORABLE
Favorable report first modification
What subject areas will I address in this grade?
The Degree in Computer Engineering is organized into the following modules:
| MODULE | ECTS CREDITS | CONTENTS |
| 1. Common Core Knowledge Module | 24 | This module includes the subjects common to all the degrees that can be taken at the URJC. |
| 2. Branch basics module | 36 | Here the basic training subjects for the degrees of the Engineering branch, in which this Degree is framed, are grouped. |
| 3. Mandatory knowledge module | 120 | This module includes the subjects that make up the main body of the degree. |
| 4. Optional knowledge module | 72 (only 24 are attended) | Here are subjects that complement the student's training, allowing him to achieve a certain degree of specialization in the chosen subjects. |
| 5. External internship module | 15 | The student will carry out internships in companies or institutions in which they will develop activities that will complement their training. |
| 6. Academic credit recognition module | 6 | This module is passed through the participation of the student in sports university activities, student representation, solidarity and cooperation. |
| 7. Final Degree Project Module | 15 | As the last subject, the student will carry out a Final Degree Project in which they will put into practice the skills acquired throughout the degree. |
The subjects of modules 1, 2, 3 and 4 are included in the following subjects:
| RAW MATERIAL | ECTS CREDITS (MANDATORY / OPTIONAL) |
| 1.1. Humanities | 6 / 0 |
| 1.2. Basic Legal Principles: Professional Ethics and Equality | 6 / 0 |
| 1.3. Introduction to programming | 6 / 0 |
| 1.4. Language | 6 / 0 |
| 2.1. Math | 18 / 0 |
| 2.2. Physical foundations of computers | 6 / 0 |
| 2.3. Statistics | 6 / 6 |
| 2.4. Operational and Statistical Management Methods | 6 / 0 |
| 3.1. Object-oriented programming | 18 / 0 |
| 3.2. Computer Engineering | 24 / 12 |
| 3.3. Databases | 6 / 6 |
| 3.4. Computer networks | 12 / 6 |
| 3.5. Operating Systems | 12 / 0 |
| 3.6. Software Design Fundamentals | 6 / 0 |
| 3.7. Human-computer interaction | 6 / 6 |
| 3.8. Distributed application development | 6 / 0 |
| 3.9. Direction and Project Management | 6 / 0 |
| 3.10. Artificial intelligence | 6 / 6 |
| 4.1. Information systems | 0 / 6 |
| 4.2. Computer Graphics | 0 / 18 |
| 4.3. Algorithms and Computability | 0 / 6 |
Recommended Income Profile
The type of activity to be carried out by these engineers will require in-depth knowledge of the architecture and structure of computers and digital data processors, of operating systems, of networks, of the specific problems of developing embedded systems and of the development of applications in which it is critical to take advantage of the capabilities of the system to achieve cost/performance compromises that guarantee the success of the system (typical examples today could be video game consoles, mobile phones, medical imaging equipment, large infrastructures for scientific calculation, distributed systems, etc.). For these reasons, the recommended profile is that of a student interested in the world of hardware and computer systems.
On the recommended income profile, no restriction is placed other than that established by law (PAU). However, according to the objectives of the training program and the study plan of the degree, it can be established that the ideal entry profile, from an academic point of view, is that of students with good training in basic engineering tools, such as mathematics and physics.
Objectives
The fundamental objective of the Degree in Computer Engineering from the Rey Juan Carlos University is to train highly qualified engineers in digital hardware and software design of complex systems, including communication systems, parallel and distributed architectures, computers and all kinds of devices. Graduates will obtain solid scientific foundations in the areas of programming, distributed architectures and digital systems, enabling them to analyze, design, adapt, modify, implement, manage and integrate capabilities, specific hardware solutions and embedded software with the aim of improving existing technologies. . To do this, graduates will be trained to analyze and discover the fundamental aspects of a problem to design complete computational, technological and practical solutions. In addition, graduates will obtain in-depth knowledge and the ability to lead both the development of multidisciplinary projects in the indicated field of action and the changes that occur due to being a rapidly evolving environment.
The fundamental objective of the Bachelor's Degree in Computer Engineering from the Rey Juan Carlos University is to train highly qualified engineers in digital hardware and software design of complex systems, including communication systems, parallel and distributed architectures, computers and all kinds of devices, such as telephones, MP3 players, digital video recorders, graphics cards, etc.
Graduates will obtain solid scientific foundations in the areas of programming, distributed architectures and digital systems, enabling them to analyze, design, adapt, modify, implement, manage and integrate capabilities, specific hardware solutions and embedded software to improve existing technologies or invent new ones. new.
In addition, graduates will obtain in-depth knowledge and the ability to lead both the development of multidisciplinary projects in the indicated field of action and the changes that occur due to being a rapidly evolving environment.
Competences
GENERAL COMPETENCIES
- CG1 Ability to conceive, draft, organize, plan, develop and sign projects in the field of computer engineering whose purpose, in accordance with the knowledge acquired as established in section 3.2, is the conception, development or exploitation systems, services and computer applications.
- CG2 Ability to direct the activities that are the object of projects in the field of computing
- CG3 Ability to design, develop, evaluate and ensure the accessibility, ergonomics, usability and security of computer systems, services and applications, as well as the information they manage.
- CG4 Ability to define, evaluate and select hardware and software platforms for the development and execution of computer systems, services and applications
- CG5 Ability to conceive, develop and maintain computer systems, services and applications using software engineering methods as an instrument for quality assurance
- CG6 Ability to conceive and develop centralized or distributed computing systems or architectures integrating hardware, software and networks
- CG7 Ability to know, understand and apply the necessary legislation during the development of the profession of Technical Engineer in Computer Science and manage specifications, regulations and mandatory standards.
- CG8 Knowledge of basic subjects and technologies, which enable them to learn and develop new methods and technologies, as well as those that give them great versatility to adapt to new situations.
- CG9 Ability to solve problems with initiative, decision making, autonomy and creativity. Ability to know how to communicate and transmit the knowledge, skills and abilities of the profession of Computer Science Engineer.
- CG10 Knowledge to carry out measurements, calculations, assessments, appraisals, expert reports, studies, reports, task planning and other similar computer work
- CG11 Ability to analyze and assess the social and environmental impact of technical solutions, understanding the ethical and professional responsibility of the activity of the Technical Engineer in Computer Science.
- CG12 Knowledge and application of basic elements of economics and human resource management, project organization and planning, as well as legislation, regulation and standardization in the field of IT projects
- CG13 That students have shown to possess and understand knowledge in an area of study that starts from the base of general secondary education, and is usually found at a level that, although supported by advanced textbooks, also includes some aspects that they involve knowledge coming from the forefront of their field of study.
- CG14 That students know how to apply their knowledge to their work or vocation in a professional way and possess the skills that are usually demonstrated through the elaboration and defense of arguments and the resolution of problems within their area of study.
- CG15 That students have the ability to gather and interpret relevant data (normally within their area of study) to make judgments that include a reflection on relevant issues of a social, scientific or ethical nature.
- CG16 That students can transmit information, ideas, problems and solutions to both specialized and non-specialized audiences.
- CG17 That students have developed those learning skills necessary to undertake further studies with a high degree of autonomy.
SPECIFIC COMPETENCES
- B1 Ability to solve mathematical problems that may arise in engineering. Ability to apply knowledge of: linear algebra; differential and integral calculus; numerical methods; numerical algorithms; statistics and optimization.
- B2 Understanding and command of the basic concepts of fields and waves and electromagnetism, theory of electrical circuits, electronic circuits, physical principles of semiconductors and logic families, electronic and photonic devices, and their application to solve engineering problems.
- B3 Ability to understand and master the basic concepts of discrete mathematics, logic, algorithms and computational complexity, and their application to solve engineering problems.
- B4 Basic knowledge of the use and programming of computers, operating systems, databases and computer programs with application in engineering.
- B5 Knowledge of the structure, organization, operation and interconnection of computer systems, the fundamentals of their programming, and their application to solve engineering problems.
- B6 Adequate knowledge of the concept of company, institutional and legal framework of the company. Business organization and management.
- C1 Ability to design, develop, select and evaluate computer applications and systems, ensuring their reliability, security and quality, in accordance with ethical principles and current legislation and regulations.
- C2 Ability to plan, conceive, deploy and direct projects, services and computer systems in all areas, leading their implementation and continuous improvement and assessing their economic and social impact.
- C3 Ability to understand the importance of negotiation, effective work habits, leadership and communication skills in all software development environments.
- C4 Ability to prepare the technical specifications of a computer installation that meets current standards and regulations.
- C5 Knowledge, administration and maintenance of computer systems, services and applications.
- C6 Knowledge and application of the basic algorithmic procedures of computer technologies to design solutions to problems, analyzing the suitability and complexity of the proposed algorithms.
- C7 Knowledge, design and efficient use of the most appropriate data types and structures to solve a problem.
- C8 Ability to analyze, design, build and maintain applications in a robust, safe and efficient way, choosing the most appropriate paradigm and programming languages.
- C9 Ability to know, understand and evaluate the structure and architecture of computers, as well as the basic components that make them up.
- C10 Knowledge of the characteristics, functionalities and structure of Operating Systems and design and implement applications based on their services.
- C11 Knowledge and application of the characteristics, functionalities and structure of Distributed Systems, Computer Networks and the Internet and design and implement applications based on them.
- C12 Knowledge and application of the characteristics, functionalities and structure of databases, which allow their proper use, and the design, analysis and implementation of applications based on them.
- C13 Knowledge and application of the necessary tools for the storage, processing and access to information systems, including those based on the web.
- C14 Knowledge and application of the fundamental principles and basic techniques of parallel, concurrent, distributed and real-time programming.
- C15 Knowledge and application of the fundamental principles and basic techniques of intelligent systems and their practical application.
- C16 Knowledge and application of the principles, methodologies and life cycles of software engineering.
- C17 Ability to design and evaluate person-computer interfaces that guarantee accessibility and usability to computer systems, services and applications.
- C18 Knowledge of the rules and regulations of computing at national, European and international levels.
- E1 Ability to design and build digital systems, including computers, microprocessor-based systems and communications systems.
- E2 Ability to develop specific processors and embedded systems, as well as develop and optimize the software of said systems.
- E3 Ability to analyze and evaluate computer architectures, including parallel and distributed platforms, as well as develop and optimize software for them.
- E4 Ability to design and implement system and communications software.
- E5 Ability to analyze, evaluate and select the most suitable hardware and software platforms to support embedded and real-time applications.
- E6 Ability to understand, apply and manage the guarantee and security of computer systems.
- E7 Ability to analyze, evaluate, select and configure hardware platforms for the development and execution of computer applications and services.
- E8 Ability to design, deploy, administer and manage computer networks.
- E9 Ability to identify and analyze problems and design, develop, implement, verify and document software solutions based on adequate knowledge of current theories, models and techniques.
- E10 Ability to identify, evaluate and manage the associated potential risks that may arise.
- E11 Ability to describe the characteristics of the latest advances in hardware and software and their corresponding practical applications.
- E12 Ability to demonstrate awareness of the need for extensive knowledge when creating computer applications in other subject areas.
- T1 Original exercise to be carried out individually and presented and defended before a university tribunal, consisting of a project in the field of specific technologies of Computer Engineering of a professional nature in which the skills acquired in the teachings are synthesized and integrated.
Minimum stay requirements
- The permanence of the students in the Degree studies will be a maximum of eight years for full-time students. Part-time students may request an extension of up to two more years from the Rector.
- In Bachelor's degrees lasting more than 240 credits (4 years), the maximum of the previous section will be increased by one more year for every 60 ECTS credits that are added to the 240 ECTS.
- Students must pass a minimum of two subjects in the first year. Students studying part-time must pass at least one subject in their first academic year.
- Students who are studying any official Bachelor's degree at the Rey Juan Carlos University may make a maximum of four registrations to pass each of the subjects of the study plan, without counting previous cancellations of the same.
For more information see: Permanence regulations
Access and registration
Log in
Access to the official teachings of Degree will require to be in possession of the bachelor's degree or equivalent and the passing of the test referred to in article 42 of the Organic Law 6/2001, of Universities, modified by Law 4/2007, of April 12, without prejudice to the other access mechanisms provided for by current regulations.
The number of places offered for new admission are:
| Mostoles Campus: | 45 places (including transfer admission places) |
Double Degrees
|
Mostoles Campus |
Computer Engineering - Computer Engineering |
12 places |
|
Video Game Design and Development - Computer Engineering |
15 places |
Matriculation year
The enrollment process at the Rey Juan Carlos University is done through the Internet. You can carry out the procedures on the computers installed on campus or through any computer with network access. You can check the deadlines at registration , as well as the different requirements and necessary documents.
Validation with FP qualifications
Training itinerary
ACCESS THE COURSE GUIDES OF THE DEGREE
Itinerary Information (Erasmus/World)
FBC: Common Basic Training, they are validated with their counterparts of all grades
FBR: Basic Branch Training, they can be validated with their branch counterparts, taking into account the adequacy between the skills and knowledge acquired.
OB: Compulsory
OP: Optional
| COURSE 1 | |||
| Semester | Subject | Character | Credits |
| 1 | Logic and Discrete Mathematics | FBR | 6 |
| 1 | computer technology | OB | 6 |
| 1 | Physical foundations of computers | FBR | 6 |
| 1 | Introduction to Programming | FBR | 6 |
| 1 | Statistics | FBR | 6 |
| 2 | computer structure | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Calculation | FBR | 6 |
| 2 | Data structures | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Algebra | FBR | 6 |
| 2 | Computing and Society | FBC | 6 |
| Total credits to study: 60 | |||
| COURSE 2 | |||
| Semester | Subject | Character | Credits |
| Annual | modern language | FBC | 6 |
| 1 | Object-oriented programming | OB | 6 |
| 1 | Computer Organization | OB | 6 |
| 1 | Basic Legal Principles: Professional Ethics and Equality | FBC | 6 |
| 1 | Databases | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Computer Architecture | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Operational and Statistical Management Methods | FBR | 6 |
| 2 | Computer networks | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Operating Systems | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Software Design Fundamentals | OB | 6 |
| Total credits to study: 60 | |||
| COURSE 3 | |||
| Semester | Subject | Character | Credits |
| 1 | Expansion of Computer Networks | OB | 6 |
| 1 | Expansion of Operating Systems | OB | 6 |
| 1 | Embedded Systems Design | OB | 6 |
| 1 | Human-computer interaction | OB | 6 |
| 1 | concurrent programming | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Programming languages | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Distributed application development | OB | 6 |
| 2 | High Performance Computing | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Direction and Project Management | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Intelligent Systems | OB | 6 |
| Total credits to study: 60 | |||
| COURSE 4 | |||
| Semester | Subject | Character | Credits |
| 1 | Optional 1 | OP | 6 |
| 1 | Optional 2 | OP | 6 |
| 1 | Academic Recognition of Credits | OB | 6 |
| 2 | Optional 3 | OP | 6 |
| 2 | Optional 4 | OP | 6 |
| Annual | External Practices | OB | 15 |
| Annual | Final Degree Project | OB | 15 |
| Total credits to study: 60 | |||
OPTIONAL
| Course | Semester | Subject | Character | Credits |
| 4 | 1 | Mobile device lab | OP | 6 |
| 4 | 1 | Informatic security | OP | 6 |
| 4 | 1 | Advanced Algorithms | OP | 6 |
| 4 | 2 | Sequential machines, automata and languages | OP | 6 |
| 4 | 2 | computer graphics | OP | 6 |
| 4 | 2 | Robotics and Domotics | OP | 6 |
| 4 | 2 | Artificial vision | OP | 6 |
External Internships
The External Practices subject is a curricular subject whose main objective is to promote a comprehensive training of the student through the practical application of the knowledge acquired during the Degree, which facilitates direct contact with the professional activity and the opportunity to join the professional world with a minimum of experience. All practices are designed so that the students who participate in them acquire professional experience in real situations and conditions, applying the knowledge, skills and attitudes that are acquired in the training processes throughout the degree. The internships represent a decisive opportunity for the personal development and professional future of the students.
Internships are activities carried out by the student in companies, institutions and organizations; that is, in centers outside the university premises, which aim to enrich and complement your university education, while providing you with a deeper knowledge about the skills you will need once you have graduated.
The External Practices subject will consist of two phases:
- Completion of the internship period that offers professional experience related to any of the graduate profiles that are expressed in the Verification Report of the degree.
- Elaboration of the memory
Documentation:
For more information: External Internship Unit
Social Security contributions for interns starting January 1, 2024
Academic Recognition of Credits
Regulations for academic recognition of credits in undergraduate studies
Mobility programs
ERASMUS
The Erasmus program makes it easy for URJC students -both undergraduate and postgraduate- to study one or several semesters at one of the European universities with which the URJC has agreements.
These exchanges traditionally have an economic endowment thanks to the Erasmus Scholarships provided by the EU and the Spanish Ministry of Education.
WORLD
The Munde program manages mobility with universities from countries not included in the Erasmus Program.
The possibility of obtaining a scholarship or economic endowment and its amount depends, in each case, on the agreements with the universities, countries or entities that sign it.
For more information:
SICK
SICUE is a national mobility program for GRADOS university students that allows them to carry out part of their studies at another Spanish university with guarantees of academic recognition, use and adaptation to their curricular profile.
Student support programs
Orientation to future students. The University offers various orientation programs for future students: we carry out visits to high schools and secondary schools, we organize guided visits to the Campuses, we are present in the Classroom and, at the beginning of each course, we carry out welcome days to guide students new students.
academic tutorials. Each teacher carries out, within their teaching planning, academic tutorials on their subject.
Coordinator of the degree. It works to promote coherence and balance between the subjects and the workloads of the students.
mentoring program. The URJC has this program, peer tutoring, in which the students of the last years act as mentors with the first year students.
Students with disabilities. The Support Office for Persons with Disabilities offers guidance and assistance to students with special needs.
Scholarships . The Rey Juan Carlos University manages the main scholarships and annual grants, both its own and from other official bodies: Ministries, Community of Madrid, International Organizations and other entities. It also publishes and disseminates those scholarships and grants of interest to its students and graduates. Throughout the course, students receive information about them through the different communication channels established.
Job placement program. The Rey Juan Carlos University, through the External Internship Unit and the Graduates Office, organizes conferences, workshops and various actions aimed at supporting and guiding students in their job search, to improve their employability and promote job placement . The University has a Job Exchange -a platform available to companies and graduates- where institutions can carry out their selection processes.
Regulation
ACADEMIC CALENDAR
REGISTRATION
*The rates corresponding to double degrees with different degrees of experimentality will be applied as established in the new Decree 43/2022, of June 29, of the Government Council, which establishes the public prices for university studies leading to official degrees and services of an academic nature in the public universities of the Community of Madrid*
- Enrollment and permanence in URJC degree studies. Academic year 2023/24
- Enrollment and permanence in URJC degree studies. Academic year 2024-25 (effective as of June 1, 2024)
- Regulation of refund of academic fees
- Admission due to change of campus or modality, university and/or partial Spanish university studies of Degree and Double Degree of the URJC
- Public Prices
TRAINING PROCESS
- joint degrees
- academic waiver
- External internships (in force during the 21/22 academic year)
- External internships (applicable from the 22/23 academic year)
- Academic Recognition of Credits (RAC)
- TFG Framework Regulation (Approved Governing Council May 26, 2023)
- Extraordinary End of Degree Award
- Extraordinary procedure for the completion of degree studies (advance call)
REVIEWS AND REVIEWS
- Review and claim of continuous assessment in URJC degree studies
- Request for review and claim of continuous evaluation
- compensation court
Validation, adaptation of studies, recognition of credits and homologation of foreign qualifications
- Validations / Recognition degrees
- Partial validation of foreign studies
- Complementary training requirements prior to the recognition of foreign qualifications
UNIVERSITY DEGREES
VISITING STUDENTS AND FUNCTIONAL DIVERSITY
COEXISTENCE REGIME
SCHOOL INSURANCE
ASSOCIATIONS
Quality guarantee
Results report
Once the follow-up has been carried out, the quantitative information on the results obtained in the follow-up of said Degree is shown, differentiated by academic year.
Report by course:
General information collection plan
Within the quality assurance system of the Rey Juan Carlos University, the following surveys are planned:
- New students
- Teacher evaluation
- Student satisfaction
- Satisfaction of the graduates
- Labor insertion
- Causes of abandonment
- Career path:
- Second year after graduation
- Third year after graduation
- Fourth year after graduation
- Degree of satisfaction:
- Faculty with the campus and university
- Teacher with degree
- of the evaluators
- Incoming student mobility program
- Outgoing Student Mobility Program
- Administration and services staff with the university
- External internships:
- Student satisfaction
- External tutor satisfaction
- Evaluator satisfaction
Survey results:
Improvement actions
The Quality Assurance System of the Rey Juan Carlos University establishes that the degree's Quality Assurance Commission will annually analyze the information derived from the degree's indicators and prepare a report that will include improvement plans if the results so indicate.
- Improvement actions 2022/2023
- Improvement actions 2021/2022
- Improvement actions 2020/2021
- Improvement actions 2019/2020
- Improvement actions 2018/2019
- Improvement actions 2017/2018
- Improvement actions 2016/2017
- Improvement actions 2015/2016
- Improvement actions 2014/2015
- Improvement actions 2013/2014
- Improvement actions 2012/2013
- Improvement actions 2011/2012
- Improvement actions 2010/2011
Renewal of accreditation
The renewal of the accreditation represents the culmination of the implementation process of the official Bachelor's and Master's degrees registered in the Register of Universities, Centers and Degrees (RUCT). The renewal of the accreditation of official bachelor's and master's degrees is organized in three phases: self-assessment report, external visit and final assessment.
In the first phase, the university describes and assesses the status of the degree with respect to the established criteria and guidelines. The result is the Self-Assessment Report (IA) that is presented. The second and third phases are carried out by a group of evaluators external to the evaluated title.”


